Technical SEO Checklist | How To Do A Complete Technical SEO Audit
Table of contents
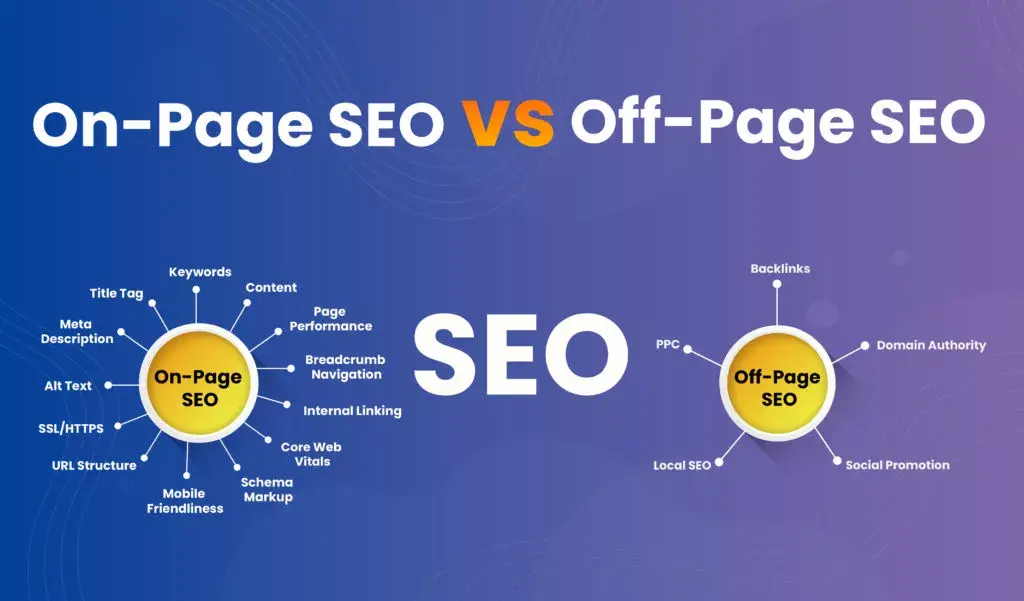
Technical SEO is the optimization of technical aspects of a website to increase its visibility and search engine results. It includes configurations that can be applied to the website and server, such as page elements, HTTP header responses XML Sitemaps redirects metadata, etc. As opposed to on-page and off-page SEO which concentrates on content and external factors like backlinks technical SEO is concerned with behind-the-scenes aspects of a site’s functioning; how search engines crawl index rank web pages.
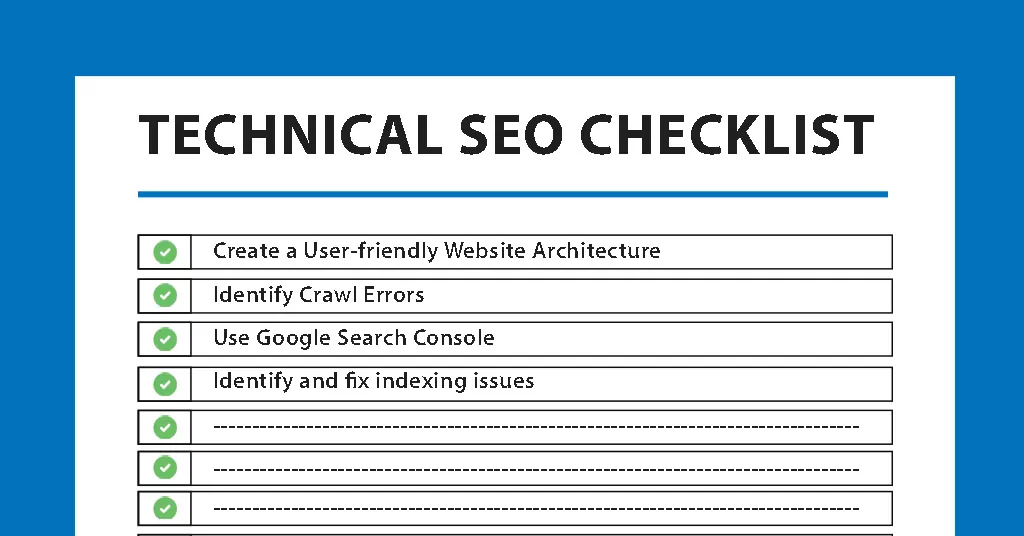
Technical SEO is incredibly important because it directly correlates with the performance of your website on search engine results. Even if your web pages contain very high-quality content, it won’t matter much unless search engines can easily crawl and understand them since no one will be able to see or find those web pages in the SERPs. This translates to lost opportunities in terms of the number of visitors and revenue for your business. Besides, Google has admitted that such factors as page speed and mobile-friendliness have an impact on rankings. As such, technical SEO plays an important role in capturing organic traffic and converting that to customers. Below is the only ultimate Technical SEO Checklist you will need in 2024:
1. Create a User-friendly Website Architecture
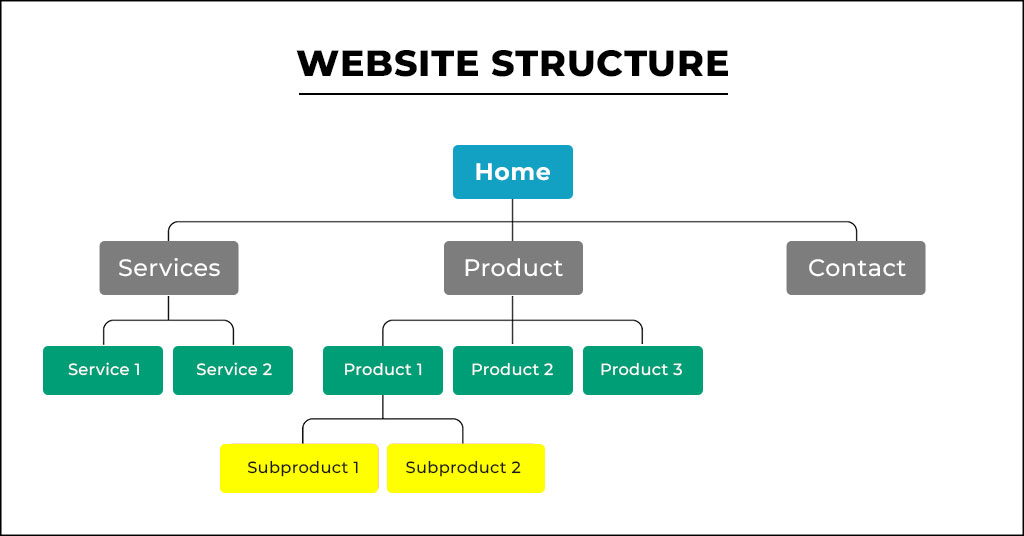
Site structure refers to the organization of information on your website. Navigability for users and crawl ability by search engine spiders are greatly improved if a site is well-structured. It entails organizing your content in a logical and intuitive, making navigation easy to understand, writing URLs that are clear enough as well as optimization of internal links so the user experience is improved. Technical SEO involves the design of a user-friendly website structure. A well-structured website not only improves the user experience of your site but also makes it more navigable for search engines. It’s a win-win situation! Below are some points to consider while creating a user-friendly website architecture:
- Plan Your Site Structure: Before picking up designing or coding your website, make sure you have a strategic plan for the site structure. This also involves knowledge of the major categories on your site, their subcategories, and how they all connect.
- Simplify Navigation: The navigation menu is the map of your website. It should be easy and user friendly where one can easily navigate through the site in a few clicks.

- Write Clear and Descriptive URLs: URLs should be easily legible and descriptive. It should provide users and search engines with a general understanding of its subject.
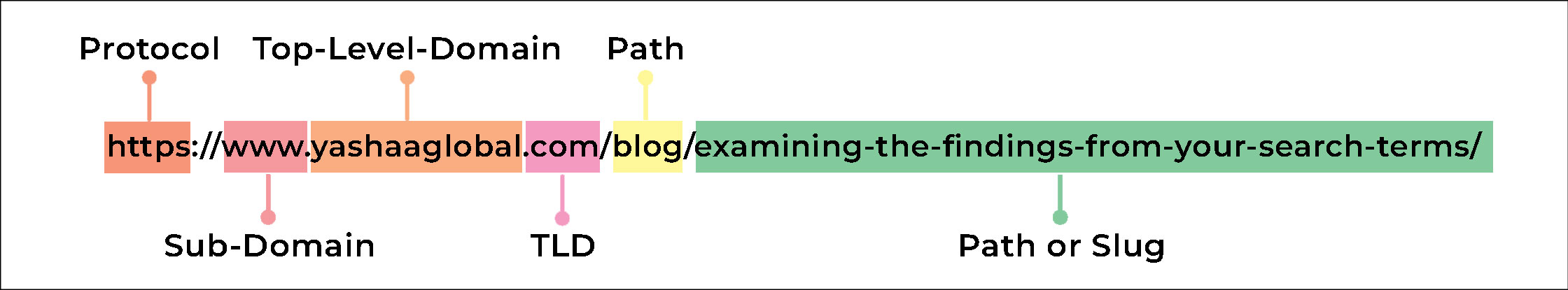
- Optimize Internal Linking: The internal links enable users to move around the website pages and it also helps search engines understand how different webpages are interlinked. A properly implemented internal linking strategy can make your website’s SEO better.
- Consider Mobile Responsiveness: As mobile devices become more popular, it is crucial that your website be responsive and deliver a good user experience anywhere.
- Use Breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs are a secondary navigation scheme that shows the user’s location on the website. They are a graphical control element used as an aid to navigation in user interfaces.
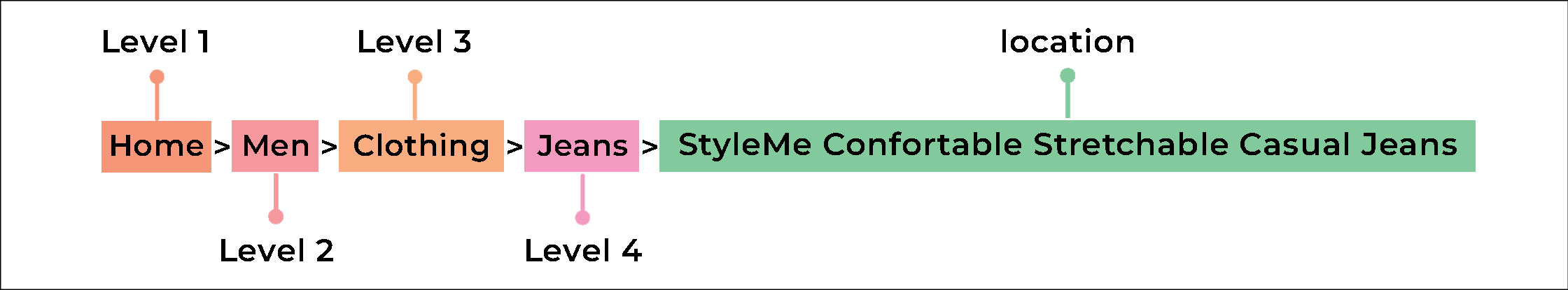
- Prioritize User Experience: Finally, a user-friendly website architecture is all about delivering pleasure to the users. The simpler it is for the users to find, what they’re looking for the more likely they are going to stay on your site and continue searching further or convert.
2. Identify Crawl Errors
Technical SEO involves identifying crawl errors as a critical step. Crawl errors happen when the bot from a search engine attempts to visit one of your site’s pages but fails. Such errors can also lead to your pages not being found, indexed, and listed on search results. All these factors are interrelated and considered quite important for the SEO result of your website. You should update and improve these elements regularly to make sure your website is both user-friendly and SEO-friendly. Here are some key points to consider:
- Crawl Error Tools: You can use tools like Google Search Console to identify crawl errors on your website. These tools will show the URLs that are generating errors, error type, and date of occurrence.
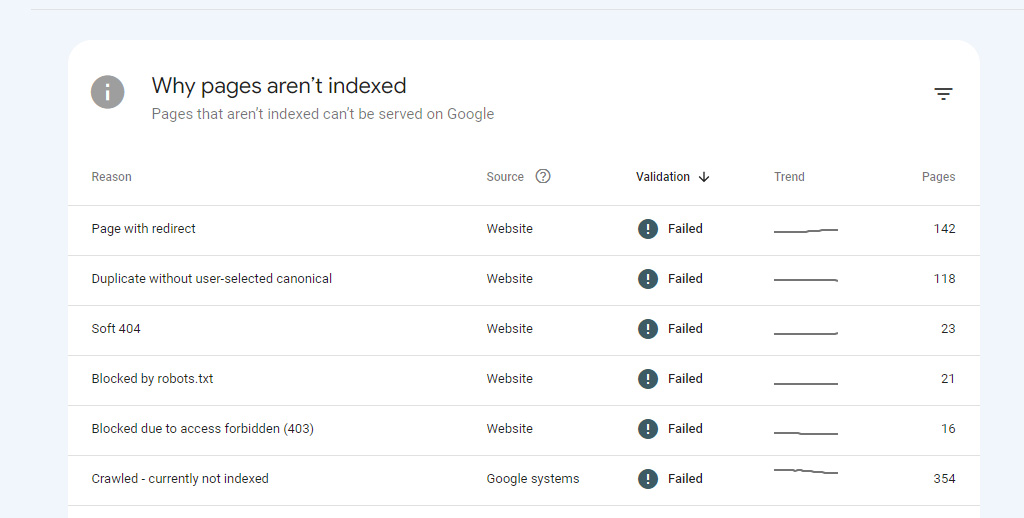
-
Types of Crawl Errors: Google categorizes crawl errors into two categories; site level and URL level.
-
Site Errors: These are the mistakes that stop search engine bots from viewing your entire website. They may be caused by DNS Errors (when a search engine cannot communicate with your server), Server Errors (if the bot fails to access your website), or Robots failure (If the bot cannot reach robots.txt file).
-
URL Errors: These are errors that take place when a search engine bot attempts to crawl some particular page of your website. The typical URL errors are 404 Not Found and Soft 404 errors.
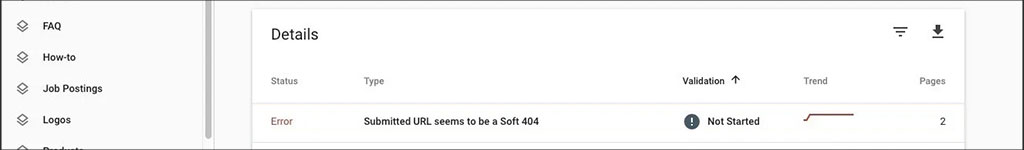
-
- Fixing Crawl Errors: Then you have to work on fixing the crawl errors. This could be done by taking out the login from pages that you want Google to crawl, checking your robots.txt file, or fixing any server or DNS errors.
- Crawl Budget: The term crawl budget means the number of pages that a search engine bot will scan and index on your website within a particular time frame. However, if you have more pages than your site can crawl in the budget provided for it, then there are unindexed pages. This is especially true for large websites that have thousands of pages or sites which often add new pages. To optimize your site’s crawl budget, make sure you speed up the loading of pages on your website; use internal links wisely and avoid creating orphanage content in addition to limiting duplicate content so that all available ones are easily accessible.
- JavaScript: JavaScript SEO is one of the technical aspects that make websites with much use of scripts easy to crawl, index and search engine-friendly. JavaScript, however, is not necessarily damaging for SEO but has its difficulties if search engine bots are unable to render or interpret content created by it. Thus, it is important to know how search engines handle JavaScript and what troubleshooting methods are available.
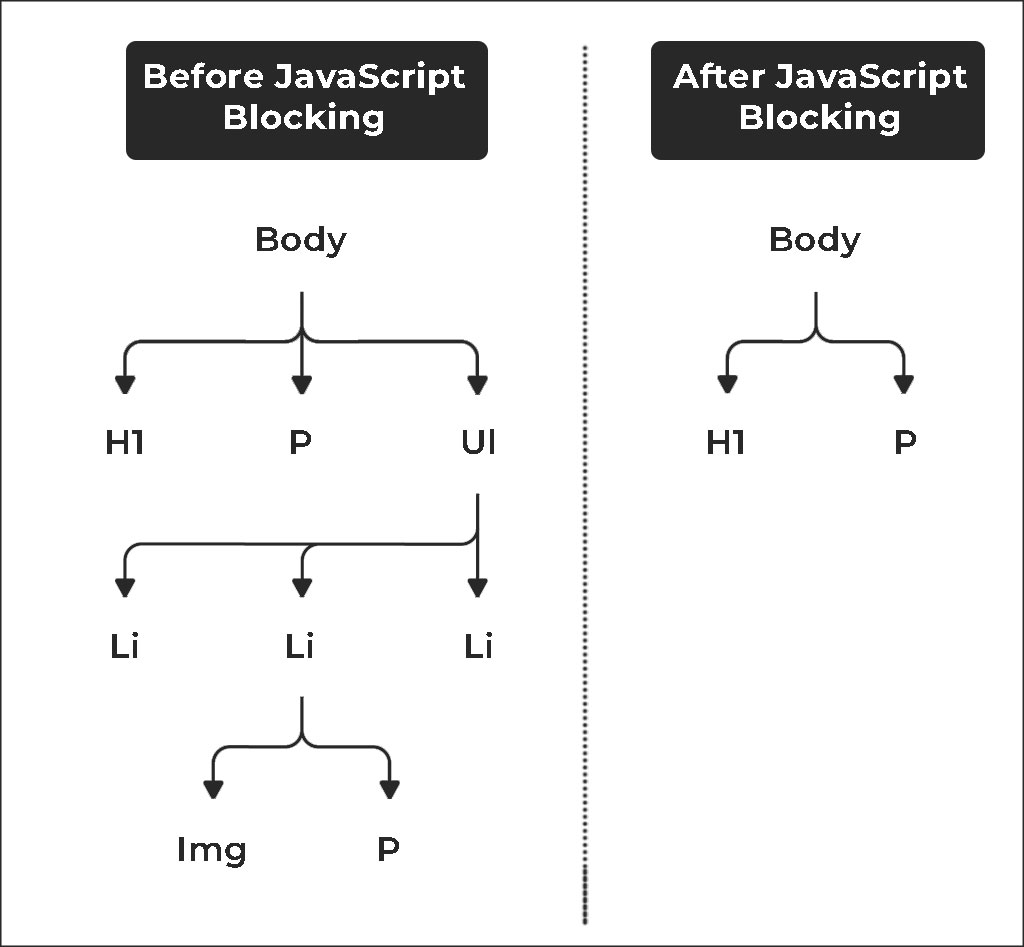
- Optimizing content injected via JavaScript: Make sure that the content added through JavaScript is easily crawlable, renderable, and indexed by search engines.
- Implementing lazy loading correctly: Lazy loading can reduce the load time of a page, but implementing it in such a way that does not harm crawling by search engines is required.
- Following internal linking best practices: Good internal linking allows search engines to understand the architecture of your website.Preventing, finding, and fixing JavaScript issues: Keep an eye on your JavaScript code and make necessary changes that may affect the SEO.
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): SSR is when JavaScript gets rendered on the server and an HTML page which has been already ready by rendering, is then served to a client. This may also improve SEO performance because it can lower the amount of time that a page’s primary content takes to load.
- Minify and compress your JavaScript files: This decreases their size, thereby increasing the load times.
- Use code splitting: With this approach, only the required JavaScript is loaded per page hence improving performance.
- Cache your JavaScript files: Employing a service worker or HTTP caching headers can increase the loading speed.
- Good Links: SEO-friendly links, also known as non-toxic or good ones, are essential for search engine optimization. They help search engines understand what your site is about and how it should be ranked, they are very important for the ranking of any given website. Useful links are simple in structure, consist of descriptive keywords, and easy to navigate. They should also be relevant and from credible sources.
- Redirects: Redirects are employed to send users and search engines to another URL other than the one they initially requested. They are vital when you change or erase content on your website. Choosing the right type of redirect (301 for permanent moves, 302 for temporary moves) is essential for keeping the SEO worth of your site.
- Server Errors: Errors that happen to servers are also known as 5xx errors and are caused by the server that hosts your website failing to deliver what the user had requested. The occurrences of server errors quite often can affect your SEO negatively since it impairs the ability of the website to become available and crawlable for Google bots. Server errors should be identified and corrected on time to preserve your site’s SEO value. Contact Jacksonville SEO Company if you cannot solve all technical SEO problems.
3. Use Google Search Console
Google Search Console is an excellent tool that gives details on how Google perceives your page. Regular tracking and maintenance of search presence in Google Search Console will allow you to find problems, eliminate them, and make your site stand out from the crowd in Google Search results. Here’s how you can use it:
- URL Inspection Tool: URL Inspection tool delivers comprehensive crawl, index, and serve information on your pages, straight from the Google index. It will help you to know if Google could crawl your page, whether it was indexed, and how it was rendered.
- Search Analytics: This functionality enables you to monitor which queries lead users to your site. You can analyze impressions, clicks, and ranking on Google Search for your site.
- Index Coverage: This report enables you to know which of your pages are indexed by Google. It can assist you in identifying and rectifying any problems that may keep your pages from being indexed.
- Mobile Usability: This report indicates any problems that may interfere with the usability of your site on mobile devices.
- Site Appearance: Google attempts to show all pages that it indexes to see the page as a user would. You can also see a text-only version of your cached page.
4. Identify and fix indexing issues
Google indexing problems are issues that prevent Google from crawling and indexing web pages. You can use Google’s Search Console and its URL Inspection tool to look for these problems. The URL Inspection tool tells you what Google sees when indexing a particular page, and you can also use it to check whether a URL might be indexable. Here are some common page indexing issues: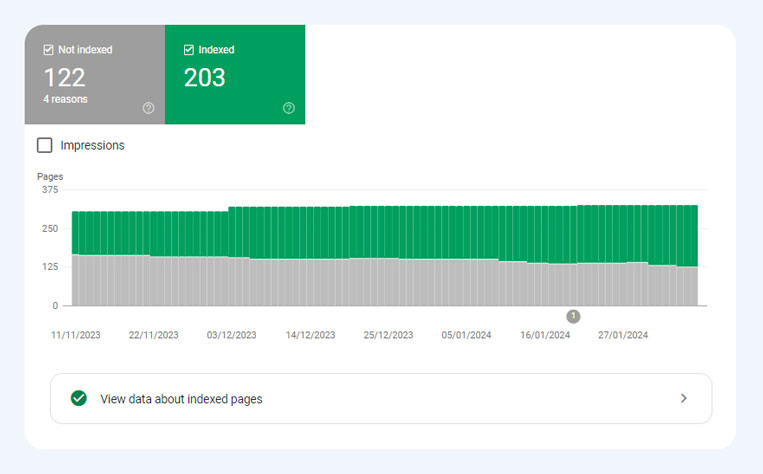
- Indexed under a different domain: Your site may be indexed under a different domain. For instance, it may be indexed as example.com rather than www.example.com Google considers example.com and www.example.com as two distinct URLs that could have different content.
- New site: If your site is a new one, Google has not yet crawled and indexed it.
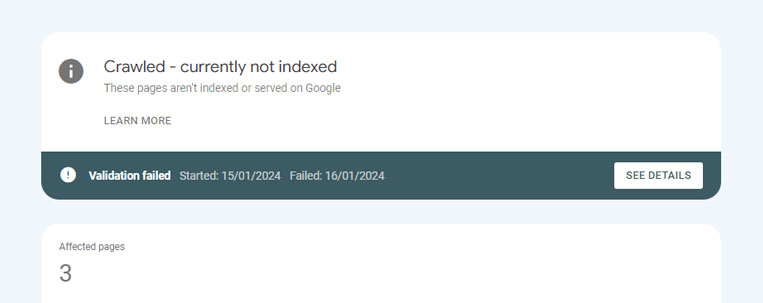
- Crawled: currently not indexed (Quality issue): This problem occurs when Google has crawled the page but not indexed it due to quality problems.
- Duplicate content: Google tries to avoid indexing multiple versions of the same content and this can cause indexing problems due to duplicate content.
- Discovered – currently not indexed (Crawl budget/quality issue): This problem arises after Google finds the URL but decides not to crawl it immediately because of the crawl budget limitation or perceived quality issues.
- Soft 404: Soft 404 errors are those that give a successful HTTP status code and the content shows that the page does not exist.
- Crawl issue: Crawl problems can keep Google from reaching and indexing a page.
- Mobile-indexing issue: This problem occurs when Google cannot index the mobile version of your site.
- Canonicalization issue: This issue arises when Google cannot determine the canonical version of the page. If you need help to solve Google Indexing Issues you can contact Jacksonville SEO experts to get rid of them.
5. Optimize Robots.txt file
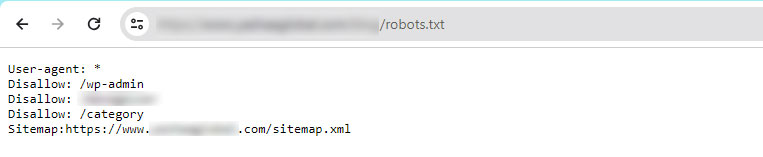
You can make your robots.txt file SEO-friendly so that search engine bots know how to crawl and index pages on your web page. Note that if you have no robots.txt file, search engines will still crawl and index your website. However, you will be unable to specify to them which pages or folders they should not crawl. Here are some steps to optimize your robots.txt file.
- Identify Pages You Don’t Want to Be Crawled: Choose which pages or directories on your site you do not wish the search engine robots to crawl.
- Create the Robots.txt File: The robots.txt file is in the root directory of your website. The basic format for a robots.txt file looks like this:
User-agent: [user-agent name]
Disallow: [URL string not to be indexed]
User-agent: [user-agent name]
Allow: [URL string to be crawled]
Sitemap: https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml- You can have different sets of instructions to allow/disallow certain URLs and include many sitemaps.
- Use Specific User-agent: To deny a particular web crawler to access a certain page or directory, indicate the user-agent name. This markup directs only the Google crawler named Googlebot not to crawl any page containing the URL string www.example.com/example-subfolder/For example:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /example-subfolder/- Check for Errors, Typos, And Mis-Capitalization: Check whether your robots.txt file has no errors or typos.
- Avoid Using Robots.txt To Hide Duplicate Content: Google makes all efforts to avoid plural content of the same category from its index.
- Be Careful of Conflicting Directives: Ensure that your robots.txt directives are not conflicting.
- Always Do a Quick Check of Your File: Please, check your robots.txt file frequently to ensure it works as you expect. You can check the Robots file in the robots.txt tester tool.
6. Use HTTPS or SSL certificates
By using HTTPS and SSL certificates, you can get a lot of advantages for your website which include improved security and protection, more user engagement and trust, better performance, and better indexing and crawling of the website. Using HTTPS and SSL certificates for your website is crucial for SEO purposes for several reasons:
- Ranking Factor: Google has officially announced HTTPS as a ranking signal included in the search algorithm of this company. Google ranks higher than websites that have HTTPS encryption.
- User Trust and Engagement: Secure user data through HTTPS connection along with the feeling of safety for site visitors is another important factor for the page experience algorithm. The presence of the obvious SSL indicators such as the padlock icon builds the confidence of the user.
- Website Performance: HTTPS site loads faster than HTTP, and thus, it ranks better.
- Data Protection: HTTPS and SSL certificates provide data encryption for data transferred between a user’s browser and a website, thus protecting it from eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Visibility in SERP: Since Google advises against searches on unsecured sites, those with HTTPS have a ranking on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERP).
7. Optimizing page title tags
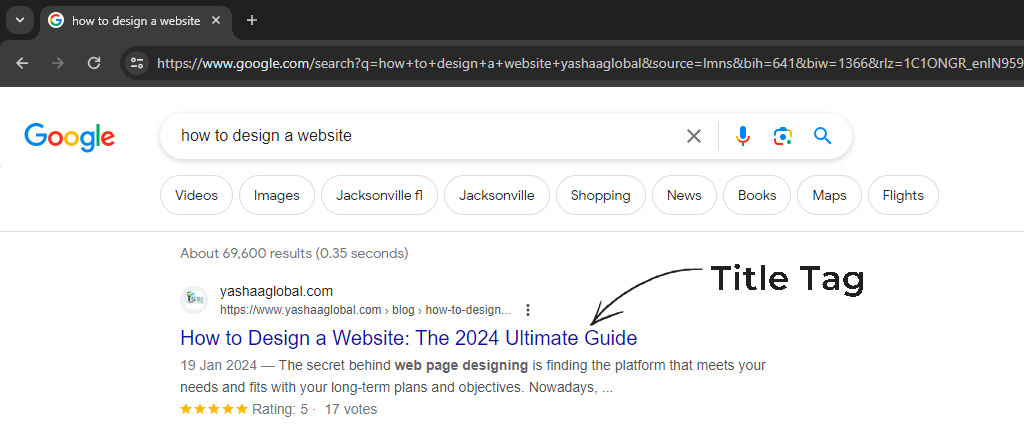
Strategically using page title tags can boost your search engine ranking, increase user engagement, give context to search engines and users, make your presence more prominent in SERPs, and improve user experience. It is crucial for Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for several reasons:
- Ranking Factor: Title tags are a minor but influential ranking factor in Google search algorithms. A good title tag optimization will make your webpage rank better on search engines.
- User Engagement: The first thing a user sees in the SERP is the title tags. By using an interesting and relevant title tag that can increase your clicks and improve your CTR, you can improve your site’s SEO.
- Relevance and Context: Title tags give search engines an idea of the content of the page. But if your title tag doesn’t include relevant keywords or phrases, you may find it difficult to rank well for related search terms.
- Visibility in SERPs: Title tags are the clickable titles in SERPs. A good title tag can help make your webpage more visible in search results.
- Social Media Sharing: Title tags can be used in the link previews that appear on social media websites, affecting how your content is presented when shared.
- Browser Tabs: Title tags inform a browser on how to display the page title in tabs making it easier for users to navigate to the correct page when they have several tabs open.
8. Optimize Your Websites For Mobile
A mobile-friendly website is a must for a pleasant user experience, better search engine rankings, more user engagement, and a wider audience. Websites need to be mobile-friendly for several reasons:
- User Experience: Responsive websites that are mobile-friendly have a better user experience. They are user-friendly on small screens, readable, easy to navigate, and interactive.
- Increased Traffic: 55% of all web traffic is generated by mobile devices. However, if your website is not mobile-friendly, you might lose a huge traffic.
- Improved Search Engine Ranking: Google treats mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor. A mobile website can assist in increasing the search engine rankings of your site.
- Higher Engagement: Mobile-friendly websites usually have features such as click-to-call buttons and map functions that allow the customers to interact with your business.
- Brand Perception: A quality mobile-friendly website will help you present your brand as more professional and respectable.
- Increased Reach: A mobile-friendly website will help you to reach a wider base.
9. Optimizing XML sitemap
A submission of an XML sitemap will not guarantee that your pages will be crawled, let alone indexed or ranked, submitting one definitely makes your chances better. Optimizing your XML sitemap for technical SEO involves several steps:
- Use Tools & Plugins to Generate Your Sitemap Automatically: Creating a sitemap is fairly easy if you have the necessary tools, such as SEO auditing software or a free online XML Sitemap generator.
- Submit Your Sitemap to Google: You can send your sitemap to Google from Google Search Console.
- Prioritize High-Quality Pages in Your Sitemap: In ranking, overall site quality is one of the important ranking factors. If your sitemap tells bots to go to thousands of poor-quality pages then search engines take these pages to mean that your site is unlikely to be a place people will want to visit.
- Remove Any Indexation Problems: Identify and eliminate any problems that prevent your pages from being properly indexed.
- Include Only Canonical Versions of URLs in Your Sitemap: This prevents problems with duplication of content.
- Use Robots Meta Tag Over Robots.txt Whenever Possible: This gives you greater control over what is crawled and indexed.
- Create Dynamic XML Sitemaps for Large Sites: For big websites, dynamic sitemaps are more preferable because they are updated automatically when new pages are added.
- Do Use XML Sitemaps & RSS/Atom Feeds: Both can be used to ensure that search engines are aware of all the pages on your site.
10. Check Your Website Loading Speed
The loading speed of a website is an important factor in technical SEO because it directly influences the user experience and search engine rankings. With attention to site speed, core web vitals, code bloat reduction, AMP implementation, and responsive design, you can greatly improve your website’s performance and SEO. Website loading speed is a critical factor in technical SEO for several reasons:
- Site Speed: The speed of a website is directly responsible for the user experience. Studies have established that users are more likely to drop a website if the loading time is more than 3 seconds. Thus, faster site speed leads to lesser bounce rates and higher user interaction.
- Core Web Vitals: Core Web Vitals are a suite of metrics developed by Google to assess the speed, responsiveness, and visual stability of a webpage. Optimizing these metrics leads to better rankings and a better user experience on the website.
- Code Bloat: Lots of sites contain useless and forgotten code that remains. With the aid of tools, you can audit and eliminate any unused CSS and JavaScript code that can greatly enhance the loading time of your site.
- AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages): AMP is an open-source framework aimed at improving the speed of web pages on mobile phones. The AMP implementation can enhance mobile user experience, decrease bounce rates, and possibly lift search engine ranking visibility.
- Responsive Design: This guarantees your site is mobile-friendly across all devices such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones. A non-mobile-friendly website is likely to give a bad user experience that ultimately affects the SERP ranking. Check Pagespeed insights to check your website speed.
11. Implement Structured Data Markup
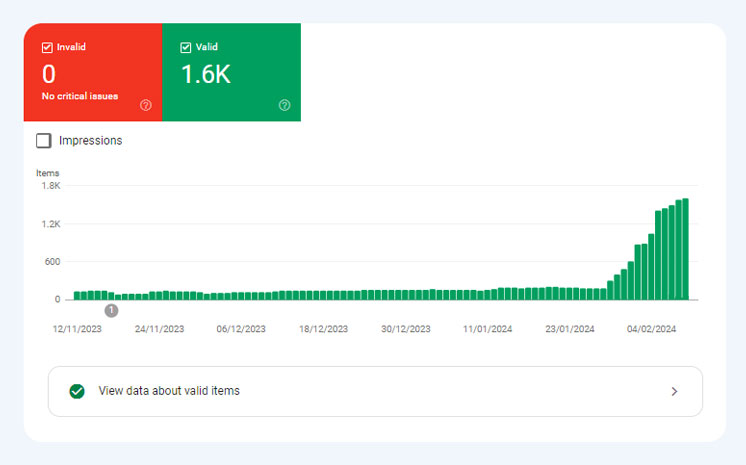
Although Google does not consider structured data by itself to be a ranking factor, it’s how you manipulate and use that structured data that influence your SEO and subsequently your site traffic, ranking, and conversion rate. Implementing structured data markup is essential for technical SEO for several reasons:
- Enhanced Understanding: Structured data provides search engines with clear directions concerning the content of your pages. It also makes search engines better understand your pages and index them properly and provides clear feedback, supplying search engines with the required information to classify web pages and their content appropriately.
- Improved Visibility: The presence of structured data increases search visibility and increases CTR. It can also optimize websites for certain search features, including rich snippets, voice search, and local search.
- Rich Results: This markup increases search engines’ comprehension of that content, which may contribute to the relevancy signals and also allows a site to benefit from improved results in SERPs such as rich snippets or knowledge graphs etc.)
- Standardization: Since this kind of markup is supposed to be parsed and interpreted uniformly by search engines and people, there are standardized implementations (formats and/or syntaxes) and classification of concepts, relationships, and terms (vocabularies) that should be used.
- User Experience: Structured data can affect user experience, click-through rates On-Page dwell time, and so on. In particular, e-commerce sites can gain a lot from using structured data with unstructured data to improve their ranking and appearance which will help in improving the User Experience. To check your structured data you can visit Schema markup validator or Google Rich Results Test.
12. Avoid 404 Pages
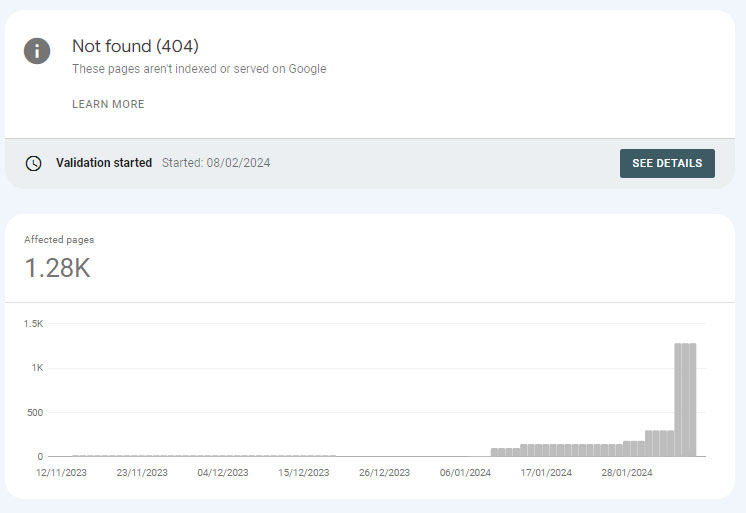
It would be a great mistake to overlook these mistakes since they have the potential to affect your SEO negatively and the user experience. Rather than letting users view a 404 error page, it is advised to direct them to a similar relevant page or enable them to contact you so that they can get the information they require. Avoiding 404 pages in SEO is important for several reasons:
- User Experience: 404 errors may result in a bad user experience, increasing your bounce rate, and likely you will be downgraded in the rankings. If users click on a link expecting to find content other than the 404 page, they will be confused.
- Lost Traffic and Revenue: If a user gets a 404 error, valuable traffic and potential revenue opportunities are lost. High-quality backlinks that point to the 404 page are essentially wasted because they lead to a dead page.
- Search Engine Trust: A high error rate on your site, often caused by many 404 errors, can make search engines distrust your site in the long run.
- SEO Equity: The fact is that error URLs may have SEO equity that you can’t get if you don’t correct them. Some SEOs suggest redirecting all error pages back to the home page or an internal category-level page to hold on to as much link juice as possible.
- Misleading Search Engines: If you redirect 404 errors to your homepage, then search engines may consider your homepage a soft 404 error. This can however result in the exact opposite of what was intended.
13. Canonicalization
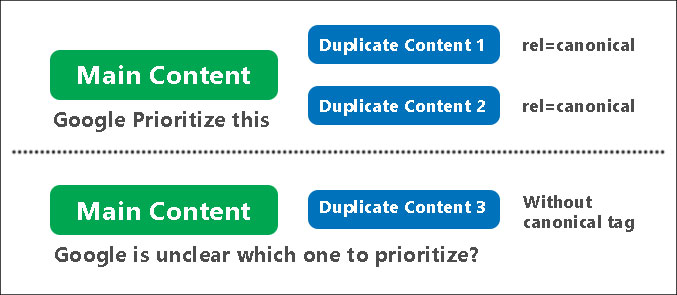
In technical SEO, canonicalization refers to a technique utilized to facilitate search engines in determining which version of a webpage is the preferred or ‘canonical’ version. This is especially relevant when several URLs can result in the same content, which may result in problems with duplicate content. Canonicalization is not just about adding a canonical tag to a page. It concerns the fact that all signals (like links, sitemaps, and even redirects) are consistent and they all point to the same canonical version.
- Avoiding Duplicate Content: The problem with duplicate content is that if the engines do not know which version(s) to index, or rank for relevant queries, the engines might end up confusing themselves. Canonicalization allows search engines to know which content is legit and should be positioned at the top.
- Consolidating Ranking Signals: It merges ranking signals for the duplicate pages. All the links, content metrics, and engagement metrics for those pages can be attributed to the canonical page.
- Controlling the Version of the Page Displayed: It lets you decide which version of a page should be shown in search results.
- Preventing Wasted Crawl Budget: Search engines have a limited crawl budget, and you don’t want them to spend it on duplicate content.
14. Pagination
Technical SEO includes pagination. The purpose of pagination is to increase website visibility and ensure a smooth user experience. Here are some key points:
- Improves User Experience: Pagination is a design strategy wherein content is separated into different pages, enabling users to navigate through long articles or large inventories of products easily. It improves user experience through facilitating navigation.
- Boosts SEO: If done right, pagination can help increase page rankings and attract more organic traffic to your site.
- Prevents Duplicate Content: The problem of duplicate content can be avoided by properly implementing pagination if you have the “View All” page and paginated pages without a proper rel=canonical.
- Avoids Thin Content: This problem of thin content can be eliminated when you put a user-friendly amount of content on each page.
- Preserves Ranking Signals: Pagination results in the splitting of internal link equity and other ranking signals, namely, backlinks and social shares, across pages. Nevertheless, this can be reduced by applying pagination only when a one-page content strategy would lead to a poor user experience.
- Enhances Website Visibility: With the help of best practices like rel tags, appropriate URL structure, consistent user interface, and optimized meta information you can make sure that search engines interpret and rate your paginated content effectively.
15. Avoiding duplicate or thin content
In SEO, it is crucial to create original and relevant content that provides value to your target audience to avoid duplicate content issues. Also, by applying the right URL structure, using canonical tags, using 301 redirects, and setting up proper meta tags, you can avoid duplicate content problems and boost the ranking of the webpage. Avoiding duplicate or thin content is crucial in technical SEO for several reasons:
- Search Engine Penalties: Google and other search engines may sanction sites that have duplicated content as it can be viewed as a way of manipulating SEO rankings.
- Unique Content: Unique material is one of the most effective means of differentiating oneself from other websites. If the contents on your website are original and that of which, nobody can lay claim to, then you are unique.
- Link Value: Duplicate content leads to a division of the link value being passed. If all the value would go to a single URL instead, it increases the likelihood that the content would rank in search.
- Crawl Efficiency: Duplicated content results in unnecessary crawling and therefore it is inefficient and may reduce the frequency of page recrawling.
- Thin Content: Thin content is poor, superficial, or meaningless content. Thin content is unique but is devoid of any meaningful or value-added content for the user.
16. Check your site for broken links
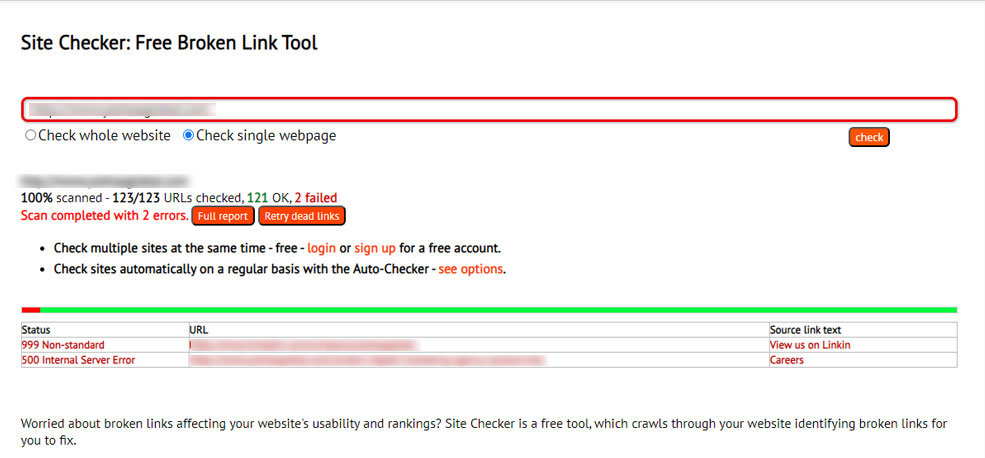
It is essential to monitor your site for broken links and fix them as soon as possible to ensure an optimal user experience and good search engine visibility. It is important for technical SEO for several reasons:
- Improves User Experience: Broken links can cause a bad user experience. If a user finds a link that does not work or a 404 error, then he or she may become irritated and leave your site.
- Affects SEO Rankings: Broken links make it impossible for search engines to crawl and index your site. This may affect your site’s ranking on search engines.
- Preserves Link Value: A broken link can lead to a fracture in the link value propagating. If all the value would go to one URL only that would increase the chances of that content to rank in search.
- Maintains Site Health: Performing link audits regularly, as well as fixing broken links without delay, ensures good online visibility while improving search engine visibility.
- Prevents Loss of Search Equity: In site migrations, a thorough 301 redirect map can avert the loss of search equity and eventually save you some time by avoiding mass broken links site-wide.
17. Avoid redirect chains
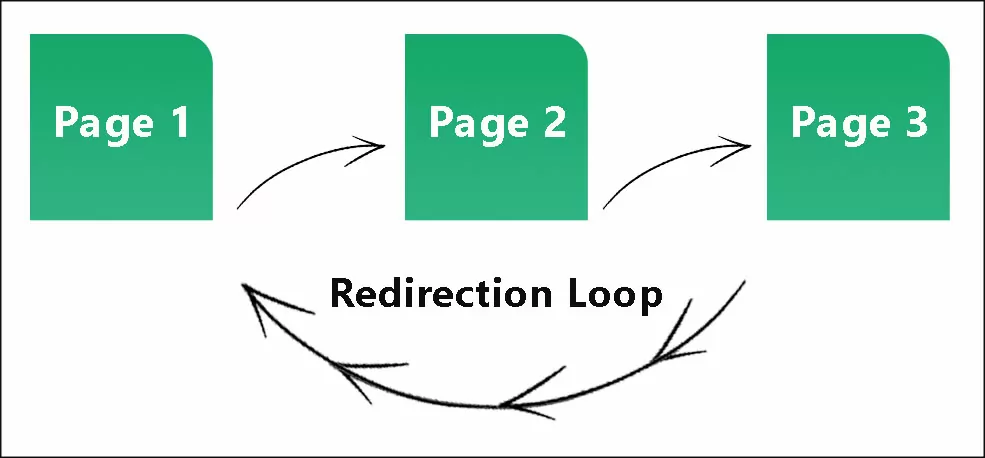
Redirect Chains take place when there is more than one redirect between the URL that is originally requested and the final URL. For instance, if you click on a link and are taken from Page A to Page B, then from Page B to Page C, and finally end up on Page D, that’s a redirect chain. Redirect chains can be detrimental to user experience as well as SEO since they reduce the speed of the process of getting users to the desired content. They increase loading times which can cause frustration among visitors who want to access information in a fast way. They also delay search engines from crawling pages as the bot would have to visit several pages before arriving at the final redirected page. It might affect the crawling of your site, which could affect indexing or at best slow down the speed of indexing. By following these steps, you can minimize the risks of getting into a redirect chain and maintain a smooth online presence:
- Do not chain several redirects together but implement 301 redirects directly from old URLs to their final destinations. This not only simplifies the process of redirection but also ensures SEO equity by passing link juice effectively.
- Do not link to a URL that you are aware is already redirecting to another URL.
- Audit your old redirects regularly.
- Utilize strong redirect tools to identify long-tail chains, break them up wherever possible, and establish URL management frameworks to minimize redirect risks. If you are having a hard time solving redirection errors on your website you can contact SEO Jacksonville experts.
18. Fix Internal and outbound links
For the internal and outbound links, you can use tools such as the “Check My Links” Chrome extension or Ahrefs Webmaster Tools to fix them. to spot and fix broken links. For internal links, you can create an internal linking architecture and use internal links in SEO tactically. For outbound links, ensure the link is related to the content. Fixing internal and outbound links is crucial for technical SEO for several reasons:
- User Experience: Broken links will have a big impact on your website’s SEO as they affect the user experience and signal outdated content. They boost bounce rates and damage your ranking potential.
- Website Indexing: Broken links hinder search engines from indexing a web page correctly. The pages that are not linked or are not accessible might not get indexed at all and hence, may lose the opportunities in search visibility.
- Page Authority: Internal links guide the PageRank flow in your site. The number of internal links a page has is directly proportional to its PageRank. But it’s not only about numbers; the quality of the link is also a crucial factor.
- Site Navigation: Internal links allow visitors to move easily around your site. They are also able to promote SEO by guiding visitors and search engines to the pages you consider significant.
- Outbound Link Relevance: Outbound links are a good source of information, references, and resources that supplement what you present in your content. They can assist in creating a strong online presence.
19. Hreflang for International Websites
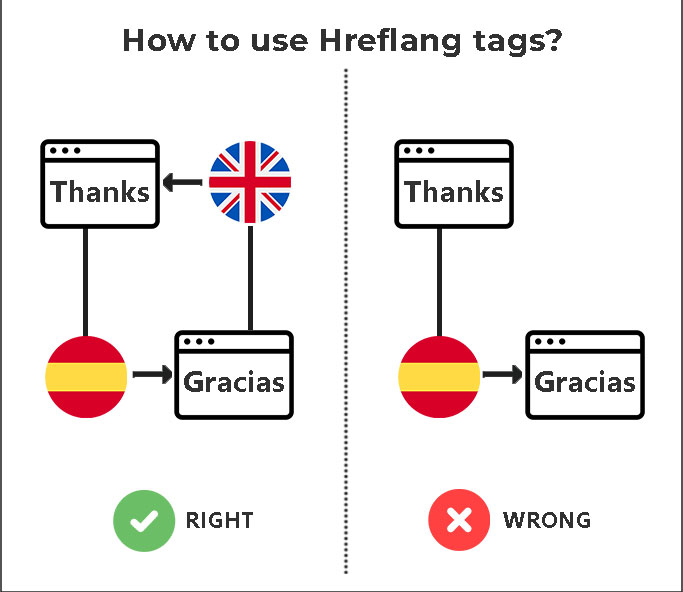
The Hreflang attribute is a hint that informs Google about the connection between international pages and which version of your page is most suitable for a user depending on their language and/or location. It is a piece of code that informs Google which language to use when providing search results to a geo-targeted audience.
- For instance, if you make a Spanish version of your English homepage, you would tag it as “es” using hreflang=“es” so that searchers with an IP address that a search engine has reason to believe is in a Spanish-speaking country will get that page in Spanish rather than the English version.
- Hreflang tags are vital for SEO as they ensure that your website remains highly relevant in Google’s eyes internationally by increasing its local relevance. They can reduce bounce rates, increase dwell times, and can directly influence your conversion rate.
- The fact is that hreflang is a signal, not a directive. This implies that other SEO factors can supersede the hreflang attribute and make another version of your page rank higher. Hence, the knowledge of their functioning and how to use them properly is key to a successful international SEO strategy.
Conclusion
Technical SEO is a core element of any website’s achievement. Even though some would consider it as a list of things, it’s about asking the right questions when you are doing a website review. The resolution of technical issues improves the performance, visibility, and user experience of a site. Here’s a quick recap –
- Website Loading Speed: Time is of the essence online. The sites that load slowly cause a high bounce rate and lost visitors. Improve server response time, shrink image sizes, eliminate render-blocking scripts, and reduce redirects. Always keep a copy of the files before you modify them.
- Website Functionality & Usability: Make sure mobile-friendly, search engine friendly URLs and correct 301 redirects after site migration. Test robots.txt, check indexed content, and optimize crawl budget. Utilize hreflang for language variations.
- Content Optimization: Repair broken links, audit internal links, remove duplicate content, and use structured data. Keep reasonable on-page links and do not canonicalize blog pages to root.
- User-Friendlier Website: Install AMP properly, include breadcrumbs for navigation, and thoroughly test on different platforms and devices.
Technical SEO is not about checking off the boxes – it is about knowing the details of your website and making it better for users and search engines alike.